Understanding Radon: Risks, Detection, and Mitigation Strategies for Homeowners
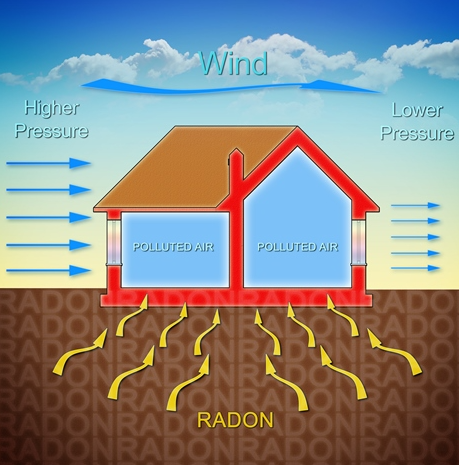
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Radon: An Invisible Hazard
- What You Need to Know About Radon Levels
- Methods of Radon Detection
- Health Implications of Long-Term Radon Exposure
- Effective Strategies for Radon Mitigation
- The Role of Ventilation in Reducing Radon Levels
- Understanding the Costs of Radon Mitigation
Key Takeaways
- Radon is a hazardous, naturally occurring gas with profound health implications.
- Homeowners should regularly test for radon and consider mitigation if levels are high.
- Professional mitigation strategies like those offered by radon mitigation Chicago can effectively reduce radon levels, protecting health.
- Community education and advocacy are crucial in promoting radon safety and awareness.
Introduction to Radon: An Invisible Hazard
Radon is the silent adversary lurking in the bowels of our homes, an invisible and odorless gas that can have severe consequences for indoor air quality and health. Originating from the natural decay of uranium found in soil, water, and rock, radon gas can seep into buildings, including homes, schools, and workplaces, through cracks and other openings in foundations, becoming trapped inside where it can build up to dangerous levels. Radon exposure is the second leading cause of lung cancer after smoking, and it is estimated to cause thousands of deaths each year. Despite its risks, many homeowners are unaware of radon’s presence because it can only be detected with specific tests. This makes radon testing a crucial safeguard for health that can reveal whether mitigative actions are warranted, and services like Radon Mitigation Chicago can assist in addressing these concerns.
Radon’s potential for harm is especially pronounced during colder months when homes are typically sealed against the weather, allowing radon levels to rise. The geographic location also influences radon prevalence, with specific areas naturally prone to higher concentrations. Therefore, it’s imperative for homeowners to check radon levels periodically and to be particularly vigilant if living in known radon-prone regions. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has a map of radon zones to help homeowners assess their potential risk. Professionals specializing in radon mitigation can help reduce radon to safer levels, ensuring that one’s home remains a haven.
What You Need to Know About Radon Levels
Radon is measured in picocuries per liter (pCi/L), a unit related to radioactive element decay. The EPA has set the action level for radon at four pCi/L. If a radon test shows levels exceeding this guideline, homeowners are urged to take remedial measures to reduce their exposure. However, it is essential to understand that even levels below this threshold can still present a risk and that the World Health Organization (WHO) recommends taking action at even lower levels, around 2.7 pCi/L. Since there is no known safe level of radon exposure, any detection of the gas should be met with consideration for mitigation, and this underscores the importance of regular testing and vigilance.
It’s worth noting that radon levels can fluctuate, influenced by factors such as barometric pressure, atmospheric conditions, and even the use of heating and air conditioning systems. This variability adds to the necessity for periodic testing—ideally once every two years or anytime changes are made to the home’s structure or heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems that could affect radon levels. Such vigilance ensures that potential long-term exposure and the corresponding health risks are minimized.
Methods of Radon Detection
Several testing options are available for assessing their home’s radon levels, each with specific benefits. Do-it-yourself (DIY) radon test kits are a convenient and economical first step, available at hardware stores and online. They involve placing a radon detection device in the lowest liveable area of the home for a specified period, usually from a few days to several months, depending on the type of detector. Upon completion, the device is sent to a laboratory for analysis, and the results are returned to the homeowner. While these kits are helpful for initial assessments, they may not be as accurate or sensitive as professional tests.
Professional radon testing is a more comprehensive alternative, where qualified technicians use advanced detection equipment to provide a detailed radon assessment. These services can be essential when buying or selling properties, as they offer both buyers and sellers confidence in the test results. Furthermore, if mitigation is necessary, professional services can guide the most appropriate and practical steps to lower radon levels within the home.
Health Implications of Long-Term Radon Exposure
The health implications associated with long-term radon exposure are significant, and their severity cannot be overstated. According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, radon is a leading cause of lung cancer deaths among non-smokers in America, and it’s estimated that in the United States, tens of thousands of people die from radon-related lung cancer each year. What makes radon particularly dangerous is its ability to damage the cells lining the lungs over time, leading to cancer. While the risk of radon-induced lung cancer increases proportionately with the level and duration of exposure, even low levels can contribute to the risk of lung cancer, especially when combined with other risk factors such as smoking.
One of the most significant difficulties in addressing the health risks posed by radon is public awareness. Many individuals need to be made aware of radon, its sources, potential health impacts, or what can be done about it. Even when aware, some may not recognize the gravity of the hazard it poses or may need clarification on the various guidelines and recommendations for action. This highlights the need for education and clear communication about radon, emphasizing the importance of testing and the availability of mitigation options.
Effective Strategies for Radon Mitigation
Mitigation is the next step for homes tested above recommended radon levels. Radon mitigation strategies can effectively reduce radon concentrations, reducing the risk of lung cancer. Typical mitigation measures include sub-slab depressurization, sealing entry points, crawl space encapsulation, and installing specialized ventilation systems. Each method is designed to reduce indoor radon levels by preventing radon entry or actively removing it from the home. Professionals in radon mitigation, such as those in radon mitigation Chicago, can determine the most appropriate solution depending on the home construction, the radon source, and the severity of the radon levels.
The Role of Ventilation in Reducing Radon Levels
Improving ventilation within a home can significantly influence indoor radon levels. By increasing the exchange of indoor air with outdoor air, radon concentrations can be diluted and, thus, minimized. Passive ventilation systems, such as vents installed in walls and floors, utilize natural airflow to help reduce radon. However, they may only sometimes be sufficient for homes with very high radon levels. Active ventilation systems, which employ fans to create pressure differences and forcefully expel radon-laden air from indoor spaces, can be much more effective. These systems are crucial to many radon mitigation strategies and effectively keep radon levels low for a long time.
Understanding the Costs of Radon Mitigation
Homeowners may be concerned about the costs of mitigating radon, as financial considerations invariably come into play. The price of radon mitigation can vary based on the size and design of the home, as well as the complexity of the installation. Generally, homeowners can expect to spend anywhere from a few hundred to a few thousand dollars to reduce radon levels effectively. This may seem like a significant expense, but weighed against the health implications of long-term radon exposure and the potential risk of lung cancer; the investment is often well justified. Moreover, there are instances when state or local subsidies may be available to help offset some of these costs. Radon mitigation systems can also bring long-term savings, potentially increasing a home’s value while safeguarding its residents’ health.




