Exploring Stomach Pain Causes, Symptoms and Treatments
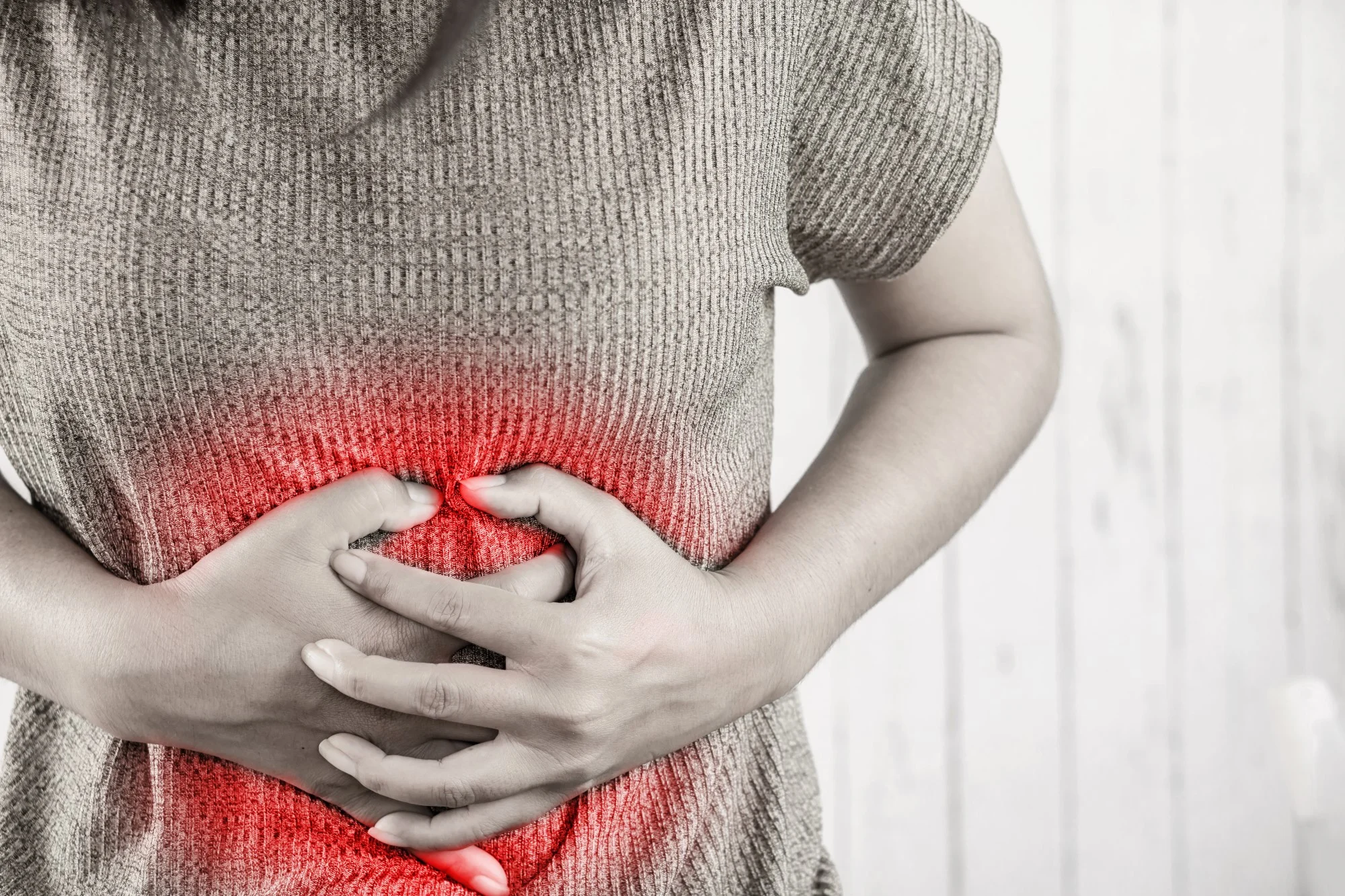
Stomach pain, also known as abdominal pain, is a common symptom that can range from mild discomfort to severe distress. While occasional stomach pain is usually harmless and may resolve on its own, persistent or severe pain may indicate an underlying health issue that requires medical attention. In this article, we’ll explore the various causes, symptoms, and treatment options for stomach pain to help individuals better understand and manage this common concern.
Causes of Stomach Pain:
Stomach pain can be caused by a wide range of factors, including:
- Indigestion: Overeating, eating too quickly, or consuming spicy, fatty, or greasy foods can lead to indigestion, resulting in discomfort or pain in the upper abdomen.
- Gastritis: Inflammation of the stomach lining, known as gastritis, can occur due to bacterial infections (such as H. pylori), excessive alcohol consumption, chronic use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), or stress.
- Gastroenteritis: Commonly referred to as the stomach flu, gastroenteritis is an infection of the stomach and intestines caused by viruses, bacteria, or parasites. Symptoms may include stomach pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and fever. Consult a gastroenterologist in Lahore for its treatment.
- Peptic Ulcers: Peptic ulcers are open sores that develop on the lining of the stomach, small intestine, or esophagus. They can be caused by H. pylori infection, chronic NSAID use, smoking, or excessive alcohol consumption.
- Gallstones: Gallstones are hardened deposits that form in the gallbladder and can cause sudden, severe pain in the upper abdomen, particularly after eating fatty foods.
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): GERD occurs when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, causing irritation and inflammation. Symptoms may include heartburn, chest pain, regurgitation, and difficulty swallowing.
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): IBS is a chronic condition characterized by abdominal pain, bloating, gas, diarrhea, and constipation. The exact cause of IBS is unknown but may involve abnormalities in the digestive tract or changes in gut bacteria.
- Appendicitis: Appendicitis is inflammation of the appendix, a small pouch located in the lower right abdomen. It typically causes sudden, severe pain in the lower right abdomen that may worsen with movement or coughing.
Symptoms of Stomach Pain:
The symptoms of stomach pain can vary depending on the underlying cause but may include:
- Localized Pain: Pain or discomfort may be felt in specific areas of the abdomen, such as the upper, lower, left, or right abdomen, depending on the underlying condition.
- Cramping: Cramping sensations or spasms may accompany stomach pain, particularly during episodes of indigestion, diarrhea, or menstrual cramps.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Feelings of nausea and the urge to vomit may accompany stomach pain, especially in cases of gastritis, gastroenteritis, or food poisoning.
- Changes in Bowel Habits: Stomach pain may be associated with changes in bowel habits, such as diarrhea, constipation, or alternating bouts of diarrhea and constipation, as seen in IBS.
- Bloating and Gas: Abdominal bloating, distention, and excessive gas production may contribute to feelings of discomfort or pressure in the abdomen.
- Fever: Infections such as gastroenteritis or appendicitis may cause fever along with stomach pain.
Treatment of Stomach Pain:
The treatment of stomach pain depends on the underlying cause and may include:
- Over-the-Counter Medications: Antacids, acid reducers, and antidiarrheal medications can help relieve symptoms of indigestion, acid reflux, or diarrhea.
- Prescription Medications: In cases of gastritis, ulcers, or GERD, proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), H2 blockers, antibiotics (for H. pylori infection), or antispasmodic agents may be prescribed.
- Dietary Modifications: Avoiding trigger foods such as spicy, fatty, or acidic foods, as well as eating smaller, more frequent meals, can help reduce symptoms of indigestion, GERD, and IBS.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of fluids, particularly water, can help prevent dehydration and promote recovery from stomach infections or diarrhea.
- Rest and Relaxation: Getting adequate rest and practicing stress-reducing techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, or gentle yoga can help alleviate symptoms of abdominal pain caused by stress or tension.
- Medical Intervention: In cases of severe or persistent stomach pain, or if accompanied by symptoms such as fever, vomiting, bloody stools, or difficulty breathing, seek medical attention promptly for further evaluation and treatment.
Conclusion:Stomach pain is a common symptom that can arise from various underlying causes, ranging from indigestion and gastritis to more serious conditions such as appendicitis or gallstones. While occasional stomach pain may resolve on its own or with home remedies, persistent or severe pain may warrant medical evaluation to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment. For more information on stomach pain and for its effective management visit a Gastroenterologist in Islamabad.